Aging: Lifespan versus Healthspan
Aging is a term that can feel both broad and overwhelming. Yet, it is also profoundly familiar. Conditions like frailty, vision impairment, muscle loss, cognitive decline are all manifestations of aging. The list seems endless. It is only when we experience these challenges firsthand, or see how our loved ones face them, that we truly begin to appreciate the weight of aging.
What is aging?
It is a complex, multifaceted process characterized by a progressive decline in physiological function and an increased vulnerability to diseases and mortality. It impacts multiple organs in our body and is shaped by genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. While the exact causes of aging remain a subject of intense research, one undeniable truth is that aging is an inevitable journey for every one of us.
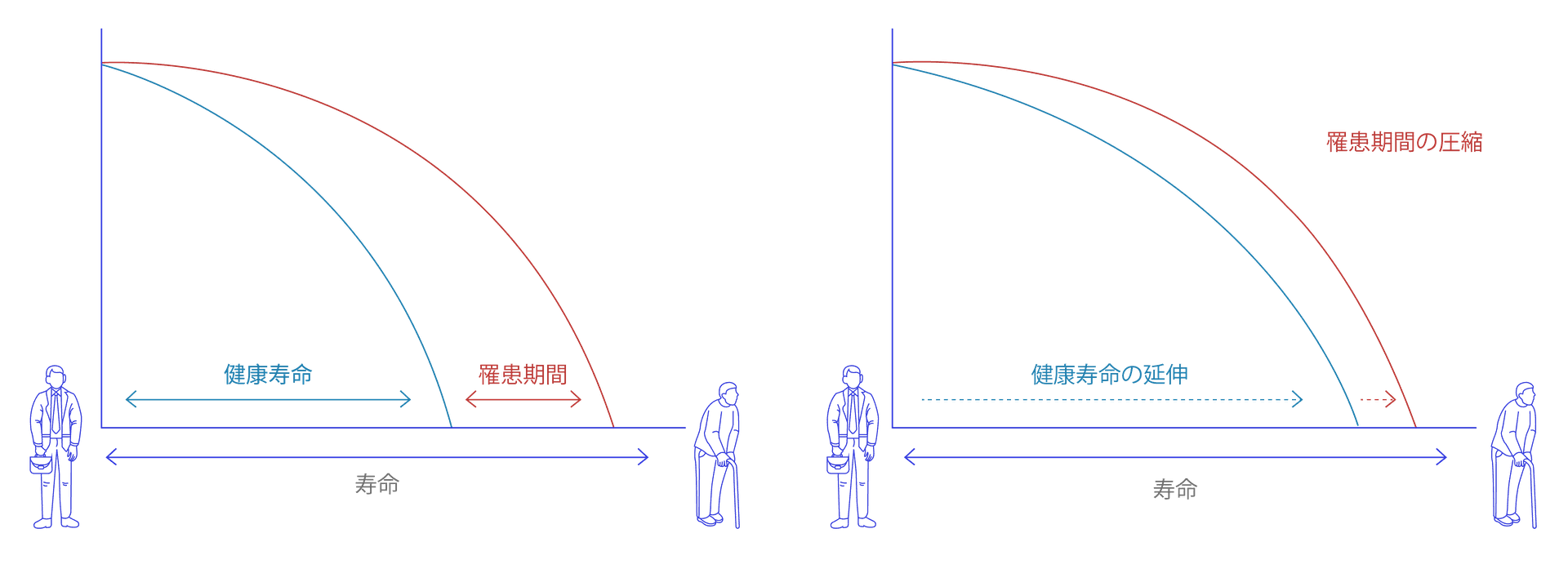
- Lifespan is the duration of life of an individual.
- Healthspan is the duration of life when an individual is fully healthy.
- Morbidity is the duration of life when an individual experiences illness or declining health.
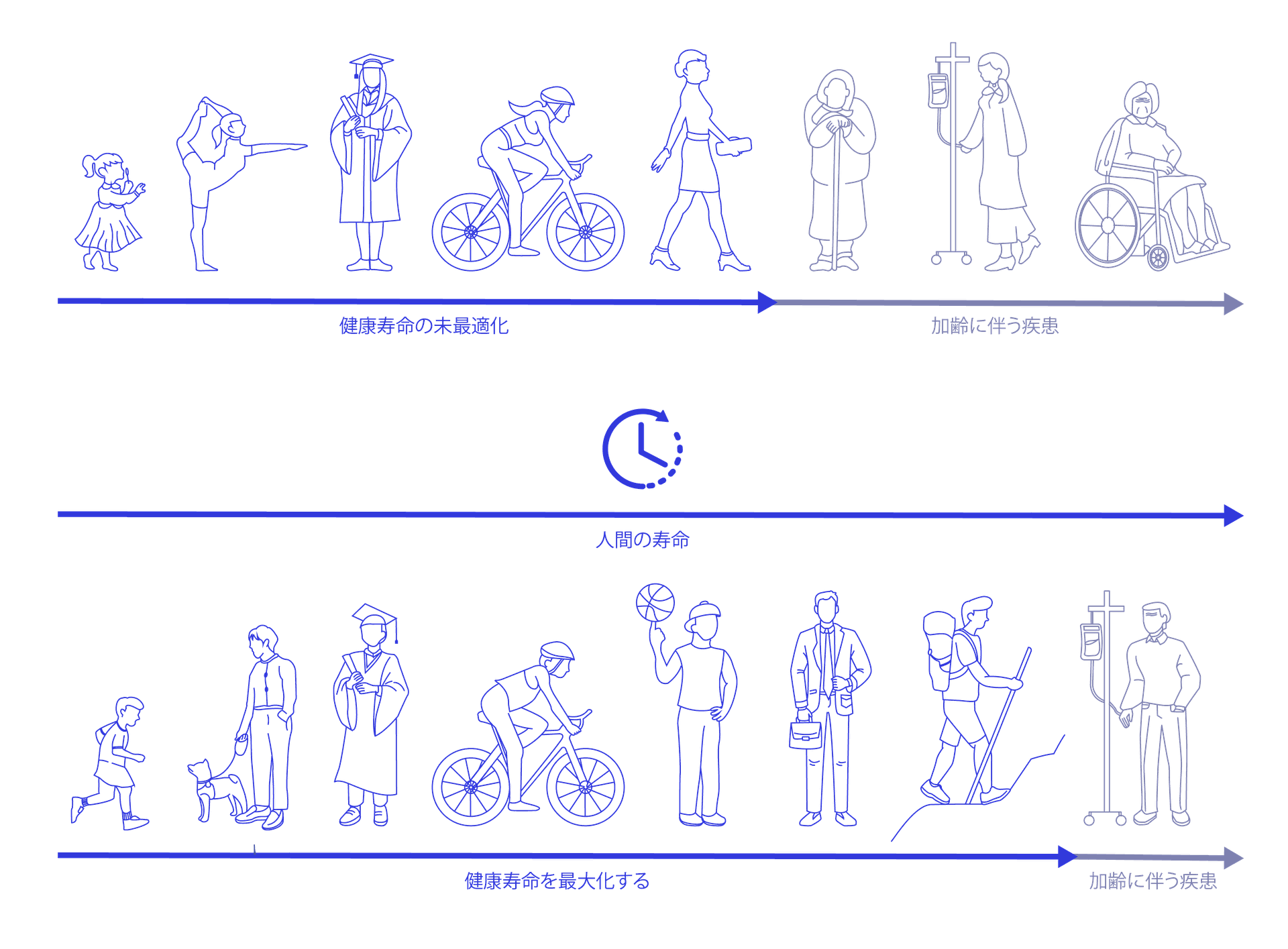
For decades, the primary focus of scientific inquiry was on extending lifespan — the total years of life. However, today the paradigm has shifted toward a more meaningful goal: extending healthspan (or ‘longevity’) — the years of life spent in optimal health, free from chronic diseases and disabilities, be they physical or mental. This resonates deeply with all of us as we reflect on the vitality and freedom of our youthful years.

At MotoGene, we are driven by the bold vision of redefining how society copes with aging. We recognize the profound burden that chronic diseases like heart failure and cancer place on individuals, particularly the elderly.
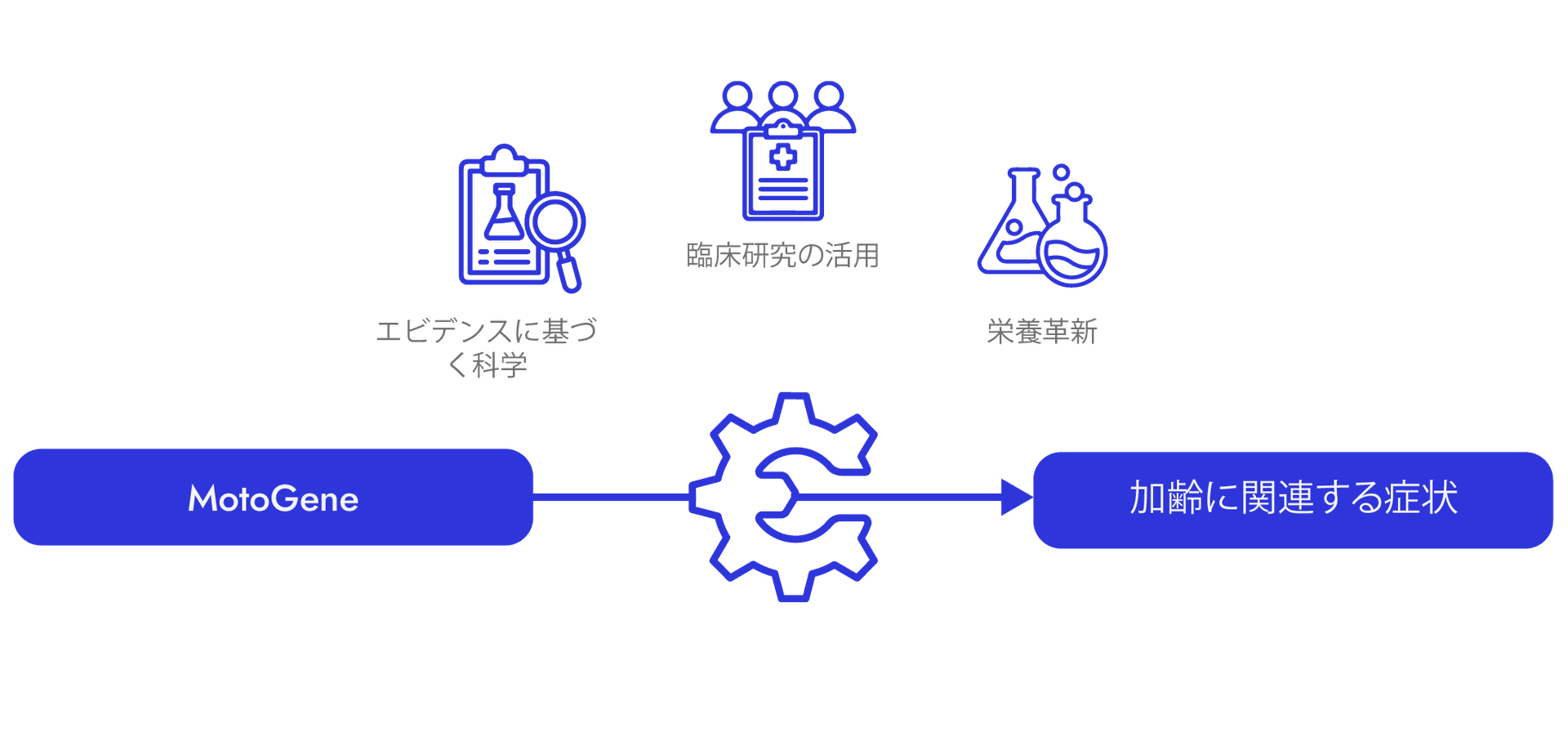
Our approach is firmly grounded in evidence-based science, leveraging clinical research and nutritional innovations.
By addressing the root causes of age-related symptoms, we aim to empower individuals to reclaim their health, resilience, vitality, and quality of life, a concept that has also been termed “healthy aging”.
UNDERSTANDING AGING:
Take Action for a Healthier Life
Recognizing the intricate nature of aging doesn’t mean we are powerless to intervene. As scientists uncover more “hallmarks of aging”, MotoGene has zeroed in on three actionable areas that are both well-researched and practical for boosting healthspan
UNDERSTANDING AGING:
Take Action for a Healthier Life
Recognizing the intricate nature of aging doesn’t mean we are powerless to intervene. As scientists uncover more “hallmarks of aging”, MotoGene has zeroed in on three actionable areas that are both well-researched and practical for boosting healthspan.
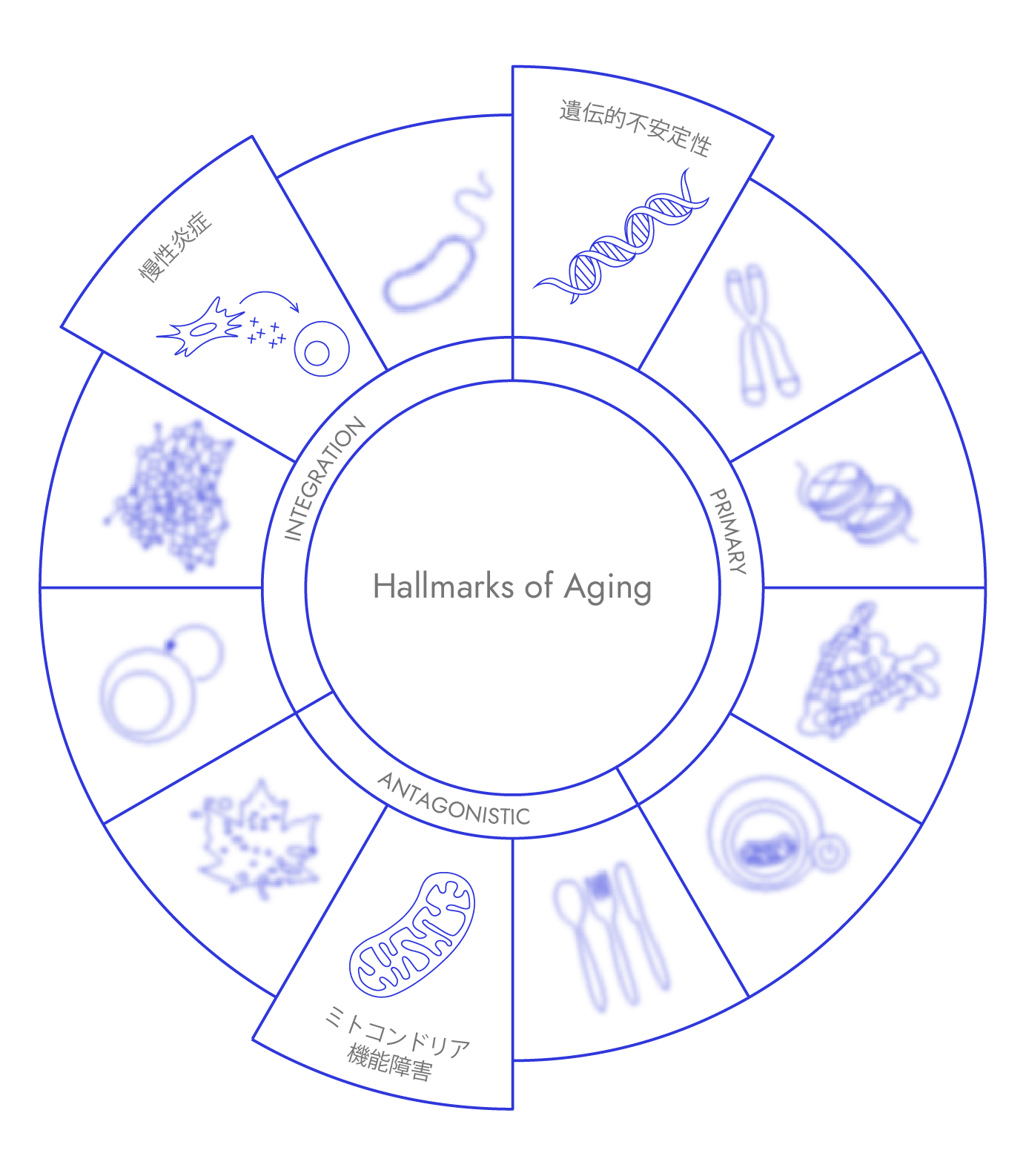
1. Genomic Instability
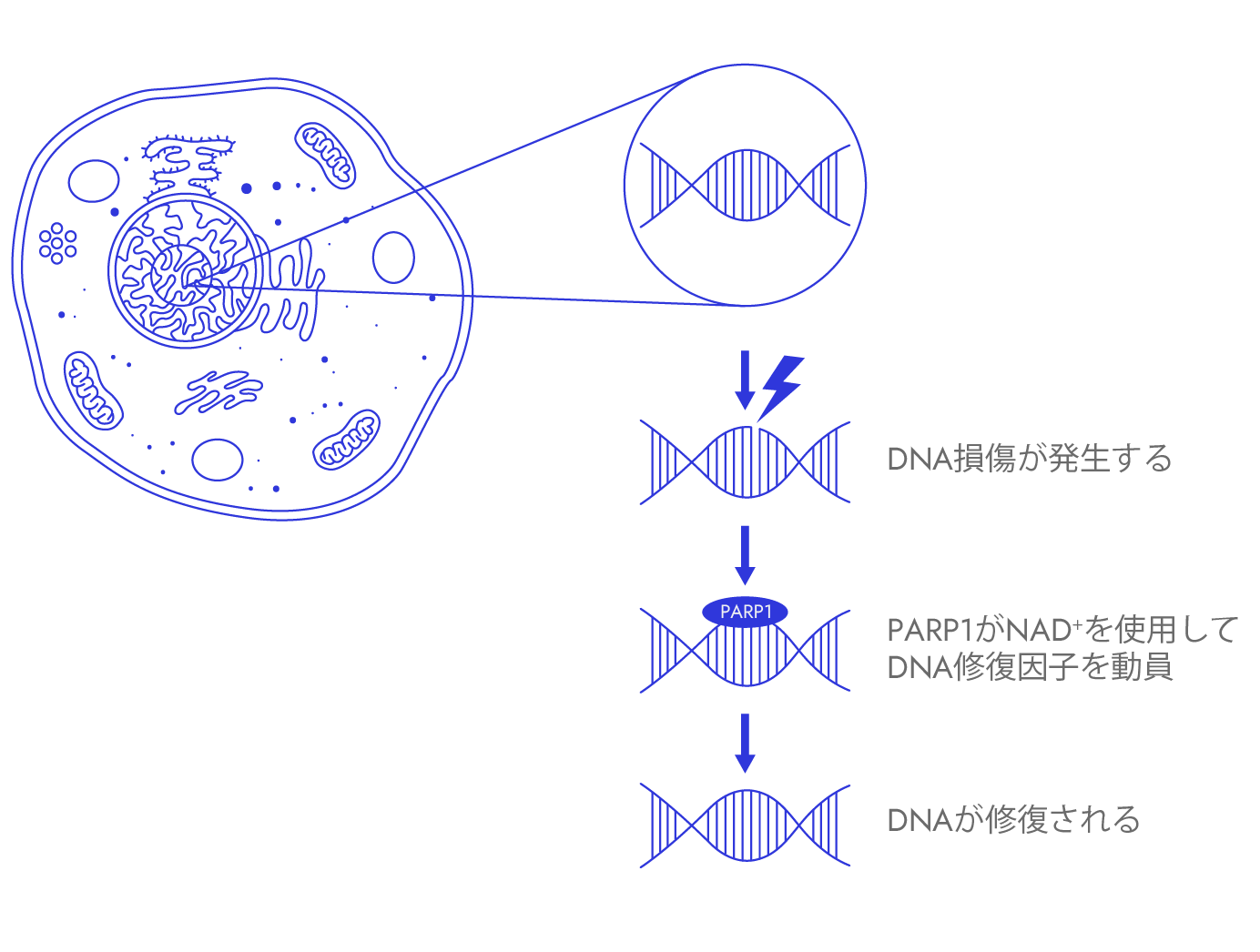
Arguably one of the most important factors impacting healthspan, genomic instability has been considered as the primary hallmark and driver of aging. Genomic instability refers to various forms of DNA damage such as DNA mutations. DNA damage can take place in either the cell nucleus or in the organelle called mitochondria. It can happen due to normal metabolic processes within our cells, spontaneous errors during DNA replication, or environmental stressors such as radiations, genotoxic drugs, smoking and infections.
To maintain healthspan, our body deploys robust repair systems to reverse the DNA damage. One main player of these systems is a DNA repair enzyme called PARP1. PARP1 ensures DNA in the cell nucleus is intact by acting as a key sensor of DNA damage and directs many DNA repair proteins to correct the damage.
Yet, it is worth noting that PARP1 activity can decline with age. Failure to promptly rectify DNA damage leads to accumulating mutation loads, which drive cellular senescence, inflammation and age-related diseases.
2. Mitochondrial Dysfunction
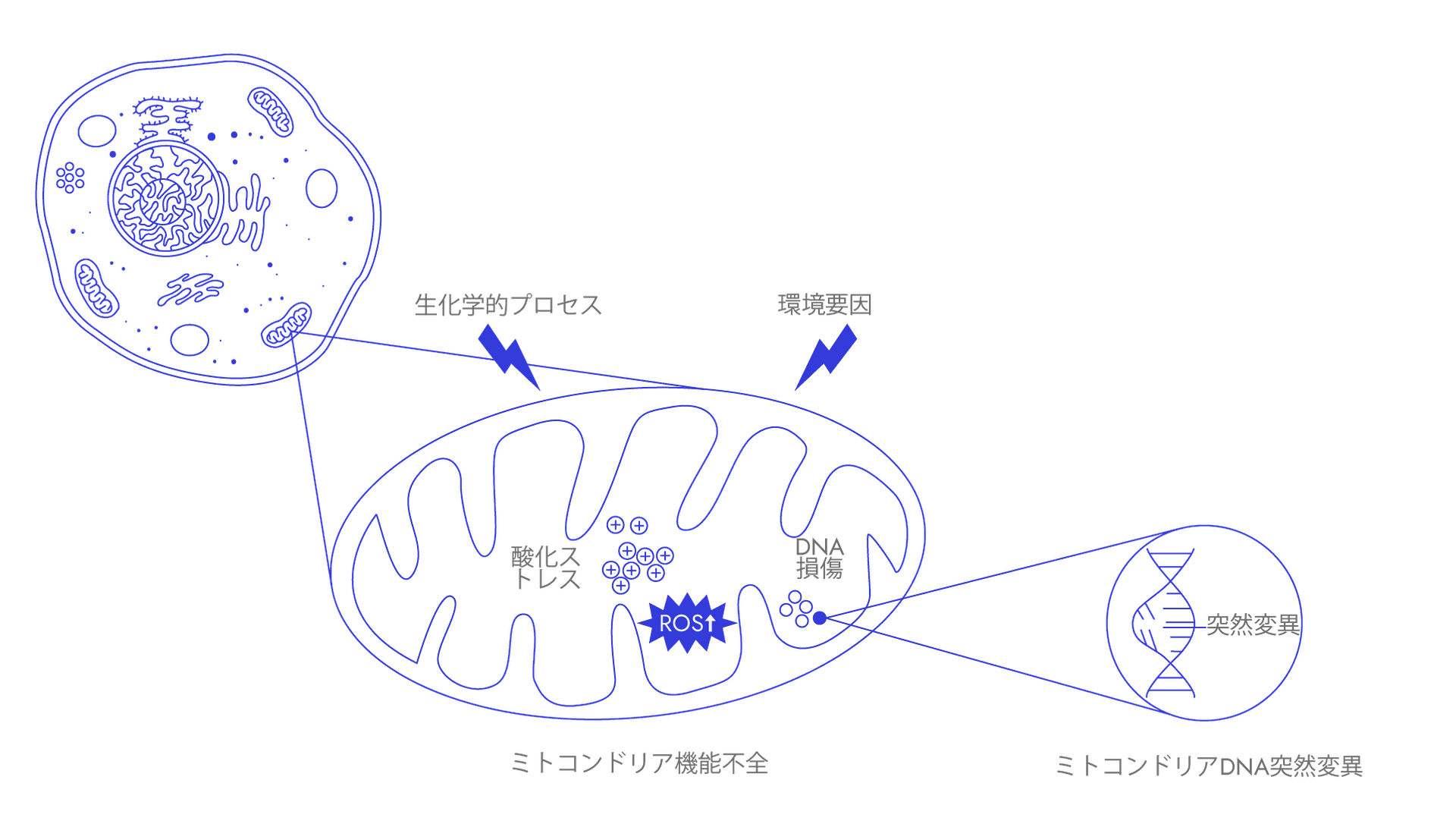
With some notable exception, each cell in our body contains many copies of mitochondria to generate energy to carry out important cellular functions. Another critical issue facing human healthspan is that mitochondrial functions tend to decline with age. This is because mitochondrial DNA undergoes mutations due to errors of the DNA replication mechanism.
Unfortunately, mitochondrial DNA mutations appear to be amplified through a process known as ‘clonal expansion’. Additional factors such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) or ‘free radicals’ and smoking, can exacerbate such phenomenon.
Mitochondrial DNA mutations are gradual. They accumulate over time, eventually reaching excessive levels and leading to defective mitochondria, poor energy production, inflammation, and predisposition to age-related diseases such as neurodegeneration.
3. Chronic Inflammation
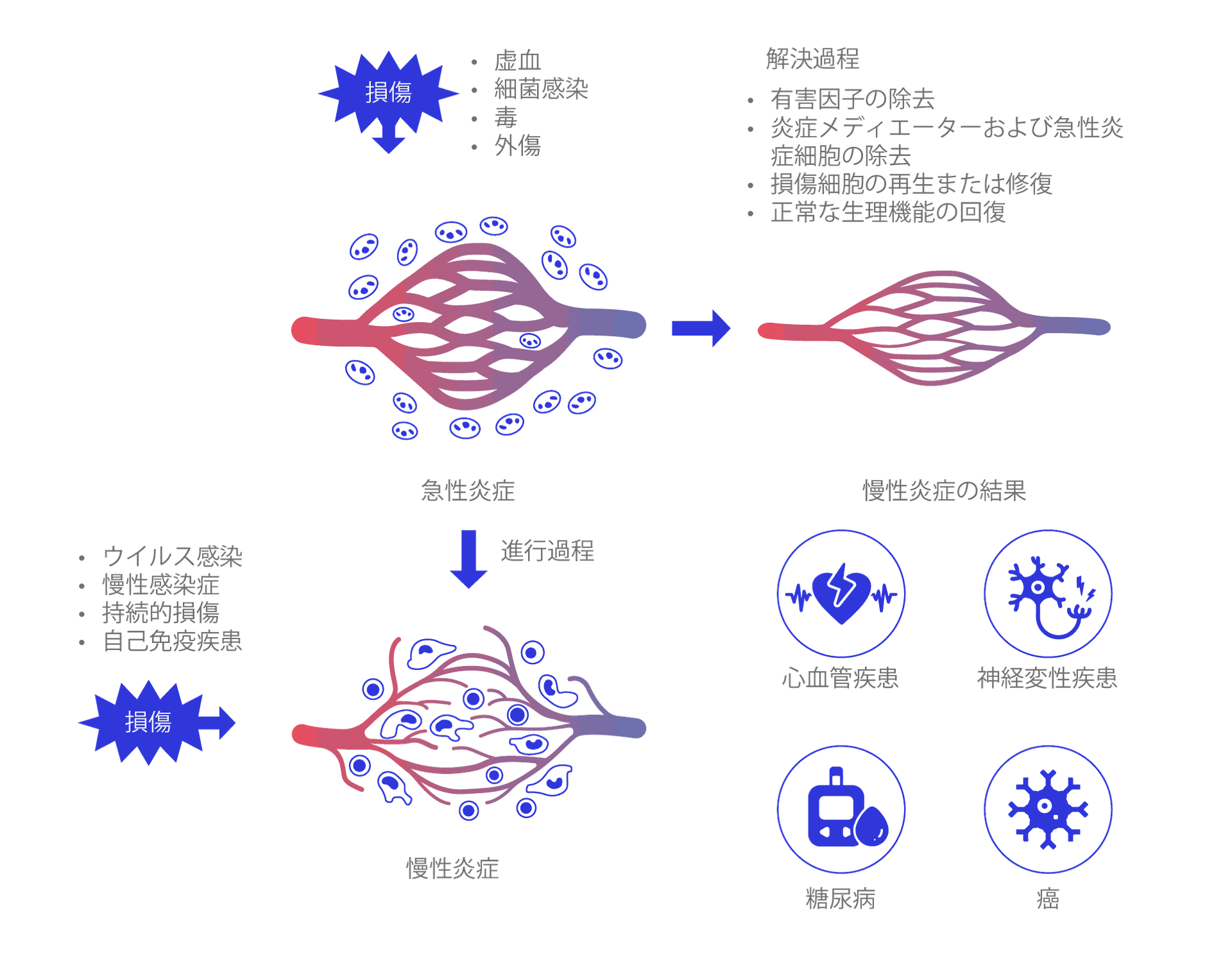
It is relatively easy to conceptualize how inflammation is essential for maintaining healthspan. For example, our immune cells rely on acute inflammation to combat infections and repair cellular injuries. However, as we age, chronic inflammation (also known as ‘inflammaging’) becomes prevalent. This persistent, low-grade inflammatory state can be triggered by various factors, including poor diets, infections, injuries, mitochondrial dysfunction, and more.
Chronic inflammation is an inherently complex topic because it involves dysfunctions at both molecular and cellular levels. For instance, it may originate from DNA damage caused by reactive oxygen species but often manifests as abnormal immune cell behavior or senescent cells in specific areas of the body. Depending on the organs affected, chronic inflammation can lead to a spectrum of age-related diseases such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders.
The consequences of chronic inflammation extend beyond impairing the body's ability to respond effectively to new challenges, such as infections. It also significantly hinders our ability to perform daily tasks, thereby reducing quality of life.
NAD⁺:
The Essential Link to Healthy Aging
At MotoGene, we recognize that the three hallmarks of aging described are deeply interconnected rather than independent processes. Through rigorous research into these key contributors to aging, we focus on identifying actionable nutritional interventions that may help slow or counteract their effects.
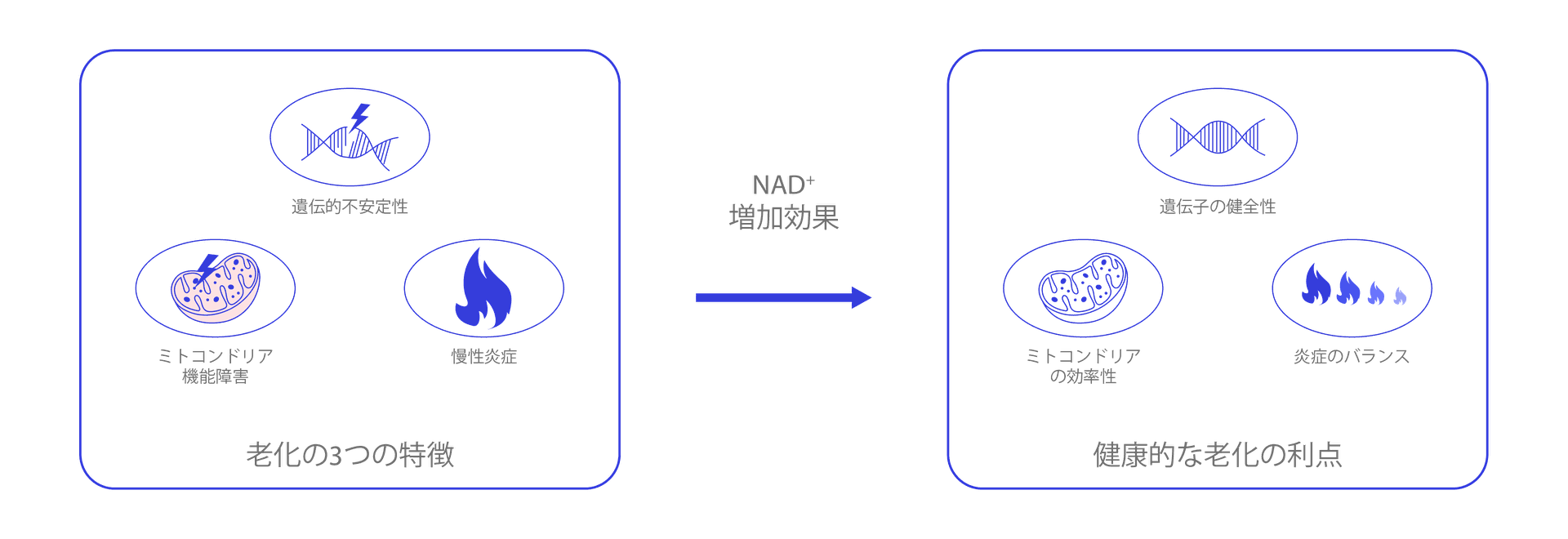
Our dedicated research has pinpointed a crucial cellular metabolite — NAD⁺ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) — as a key target in promoting healthy aging.
NAD⁺ (also known as ‘β-NAD⁺’ or ‘beta form of NAD⁺’) is a vital bioactive molecule present in all cells. It plays a crucial role in maintaining healthspan by supporting various biological processes.
1. Genomic Integrity
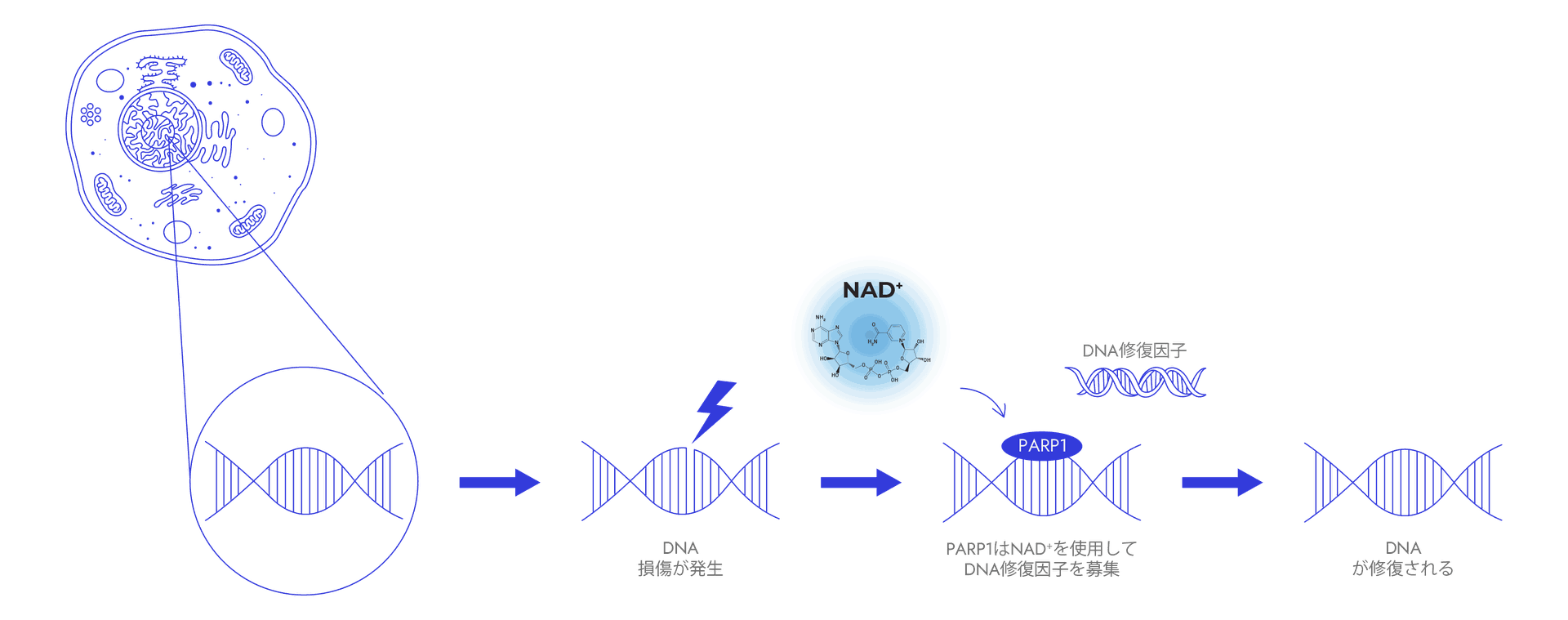
NAD⁺ plays a crucial role in maintaining genomic stability and other cellular functions by serving as a substrate for various enzymes, particularly PARP1. When DNA damage occurs, PARP1 is rapidly activated and consumes NAD+ to synthesize poly(ADP-ribose) chains on target proteins. This process acts as a signal to recruit other DNA repair proteins to the site of DNA damage.
When DNA damage is repairable, PARP1 activation promotes cell survival by engaging the DNA repair machinery. However, in cases of severe DNA damage, excessive PARP1 activation can lead to a drastic depletion of cellular NAD⁺ pools, ultimately resulting in cell death. Thus, NAD⁺ availability in cells not only influences DNA repair but also regulates other cellular processes, including cell death, inflammation and senescence.
2. Mitochondrial Efficiency
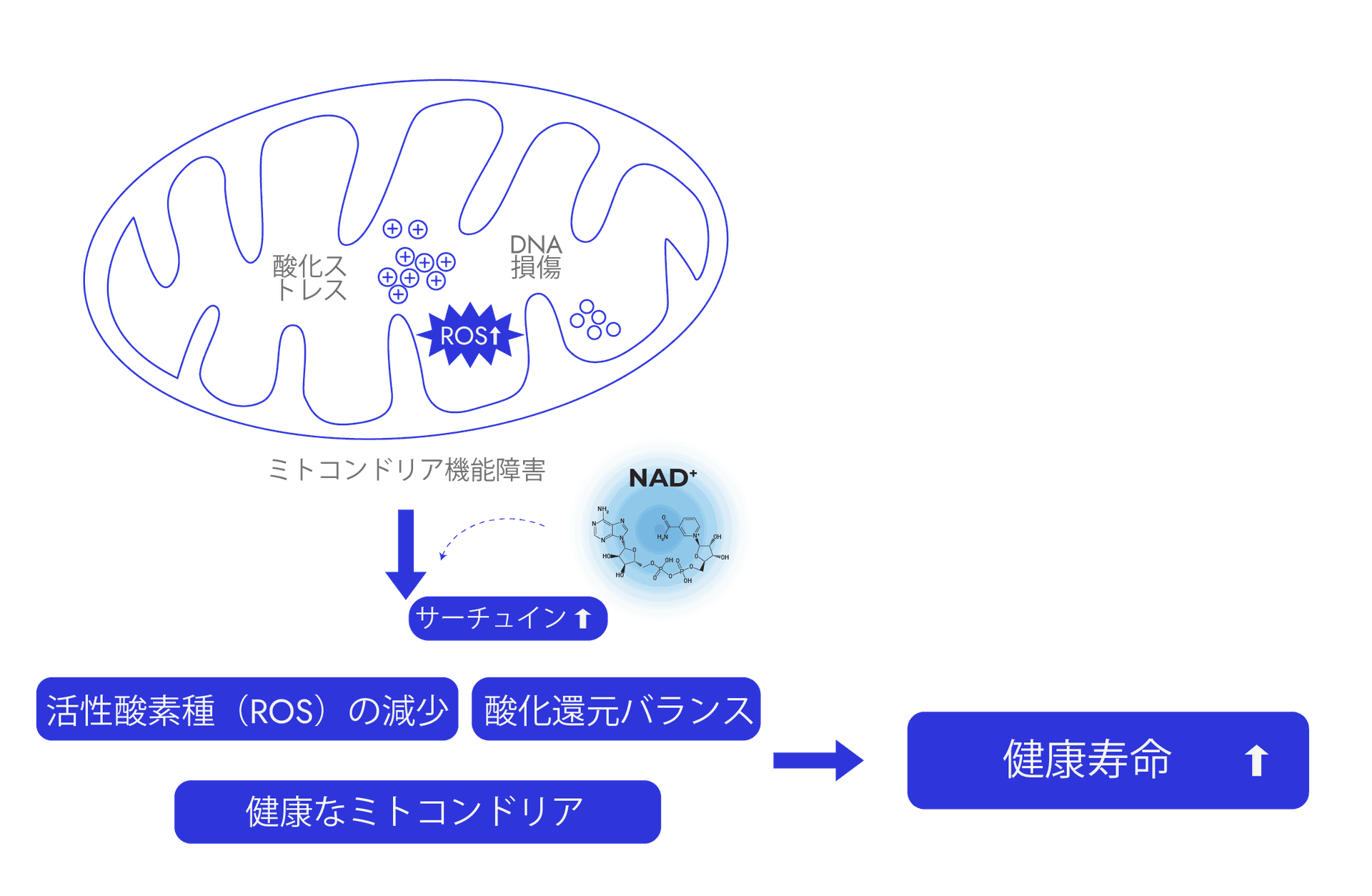
NAD⁺ is a key regulator of mitochondrial function and metabolic health. It participates in redox (or ‘reduction’ and ‘oxidation’) reactions by cycling between its oxidized (NAD⁺) and reduced (NADH) forms, driving essential metabolic processes such as glycolysis, the TCA cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, and lipid oxidation. As a vital coenzyme, NAD⁺ depletion greatly impairs metabolic efficiency and diminishes cellular energy production.
Because the NAD⁺/NADH ratio is crucial for maintaining a healthy cellular redox environment, low NAD+ levels (or excess NADH) can contribute to oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and inflammation, ultimately reducing healthspan
Beyond redox functions, NAD⁺ regulates key metabolic enzymes, including sirtuins. Sirtuin enzymes use NAD⁺ as a substrate to chemically modify mitochondrial and nuclear proteins (meaning that it removes acetyl and other acyl groups from lysine residues of the target proteins). This can alter many aspects of cells, including gene expression and mitochondrial biogenesis. Therefore, NAD⁺ availability in cells can have a significant impact on mitochondrial function and is directly linked to cellular health.
3. Balanced Inflammation
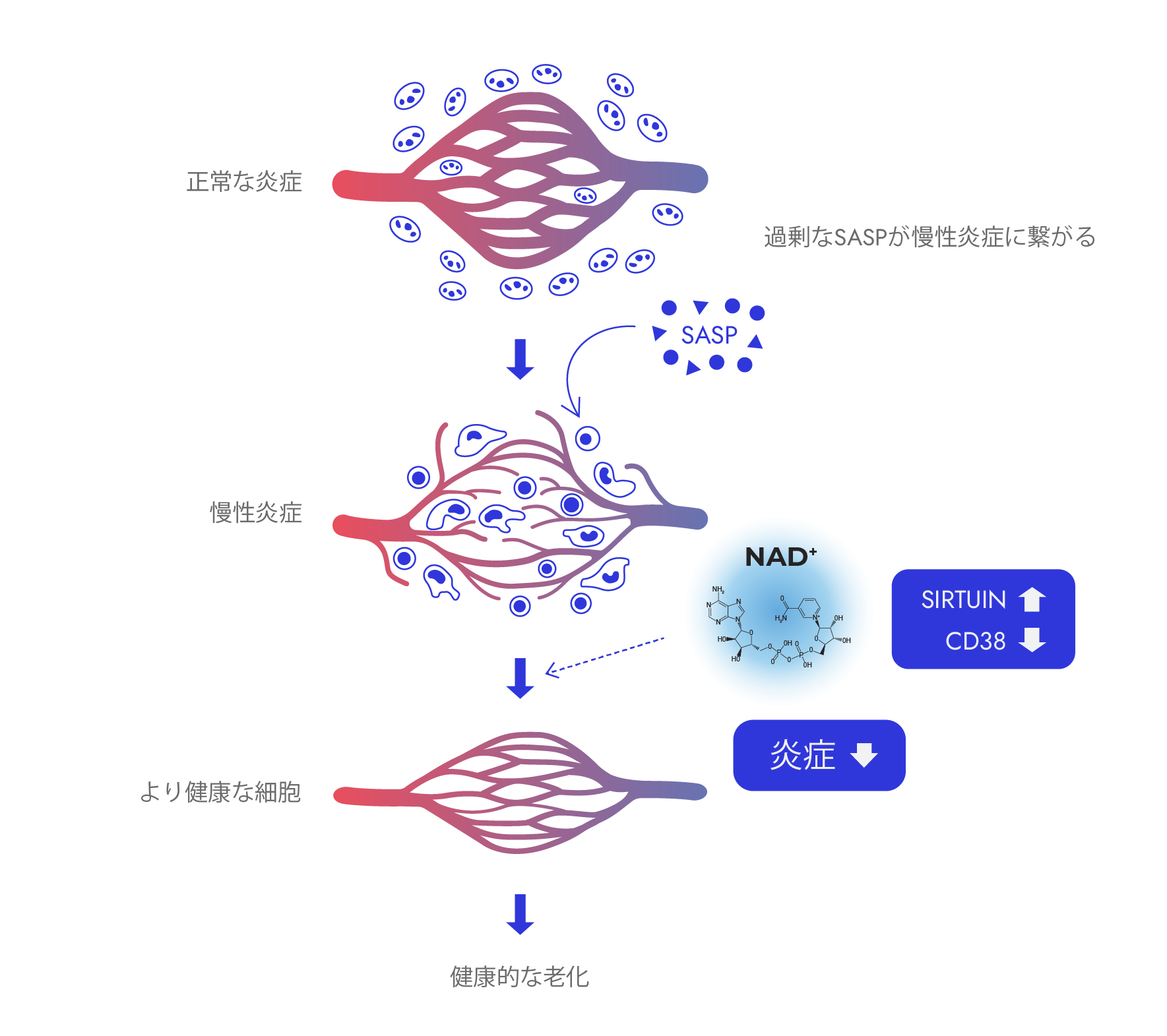
Although the mechanisms involved are intertwined and complex, NAD⁺ can exert a notable influence on the inflammatory state in our body, thereby affecting overall health.
To introduce one of the many mechanisms, NAD⁺ is utilized by sirtuin enzymes to modulate various cellular activities across different compartments, including regulating gene expression in the nucleus and metabolic processes in the mitochondria. These effects can be diverse, ranging from tuning signaling pathways that control how our immune cells secrete proinflammatory molecules (a phenomenon also known as the ‘senescence-associated secretory phenotype or ‘SASP’) to activating antioxidant defenses against oxidative stress generated by mitochondria.
Another mechanism worth mentioning is that NAD⁺ influences inflammation through the extracellular NAD⁺ consuming enzyme CD38. Reduced NAD⁺ levels, due to CD38 activity, can exacerbate ‘inflammaging.’ For instance, when CD38 is expressed on immune cells such as M1 macrophages, it can deplete NAD⁺ to the extent that perturbs mitochondrial and triggers localized tissue inflammation.
Thus, depending on the context, NAD⁺ influences different enzymes and cells to exert anti-inflammatory effects, thereby modulating the incidence of chronic inflammation and therefore healthspan.
NAD⁺ Levels in Our Body Plummet as We Age
Discussing the three key hallmarks of aging underscores the importance of maintaining adequate NAD⁺ for healthspan. Nevertheless, the relationship between NAD⁺ levels in the human body and aging warrants deeper exploration.
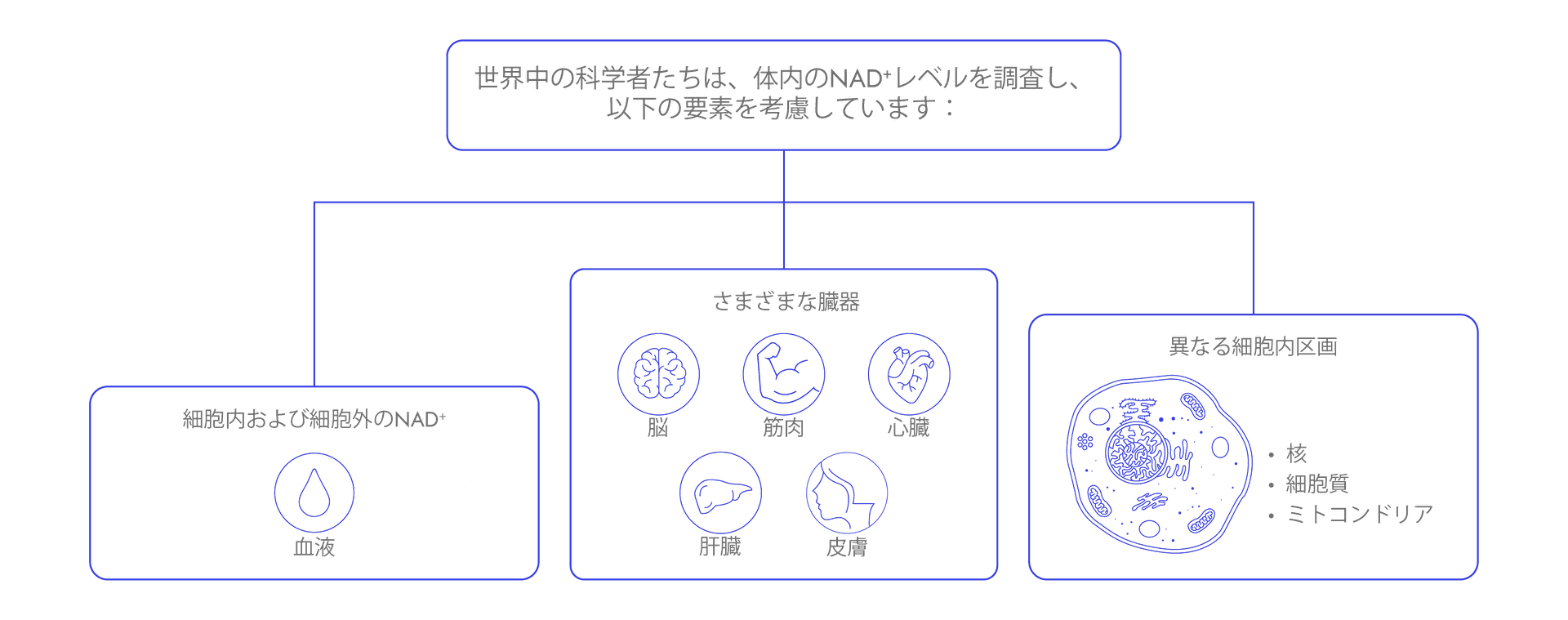
It has been observed that NAD⁺ levels tend to decline with age, although the extent of this decline vary across different individuals, potentially due to factors like genetics, lifestyle, circadian rhythm, and physiological conditions. Here, we cite a few examples to illustrate this notion.
BLOOD
Studies on blood show that plasma NAD⁺ (extracellular NAD⁺) levels decrease sharply with age, whereas whole blood NAD⁺ levels appear to significantly decline later in life. Intriguingly, women tend to have lower whole blood NAD⁺ levels compared to men, suggesting sex-specific differences in NAD⁺ metabolism.
SKIN
Human skin samples consistently display a marked decline in NAD⁺ (intracellular NAD⁺) levels with age, with some reports indicating a reduction of at least 50% over aging adults.
BRAIN
Research indicates that the brain experiences a decline in NAD⁺ (intracellular NAD⁺) with age, although the degree of reduction can vary. Some studies have reported a 10-25% decline in brain NAD⁺ levels from young adulthood to old age. Some studies, however, suggest otherwise.
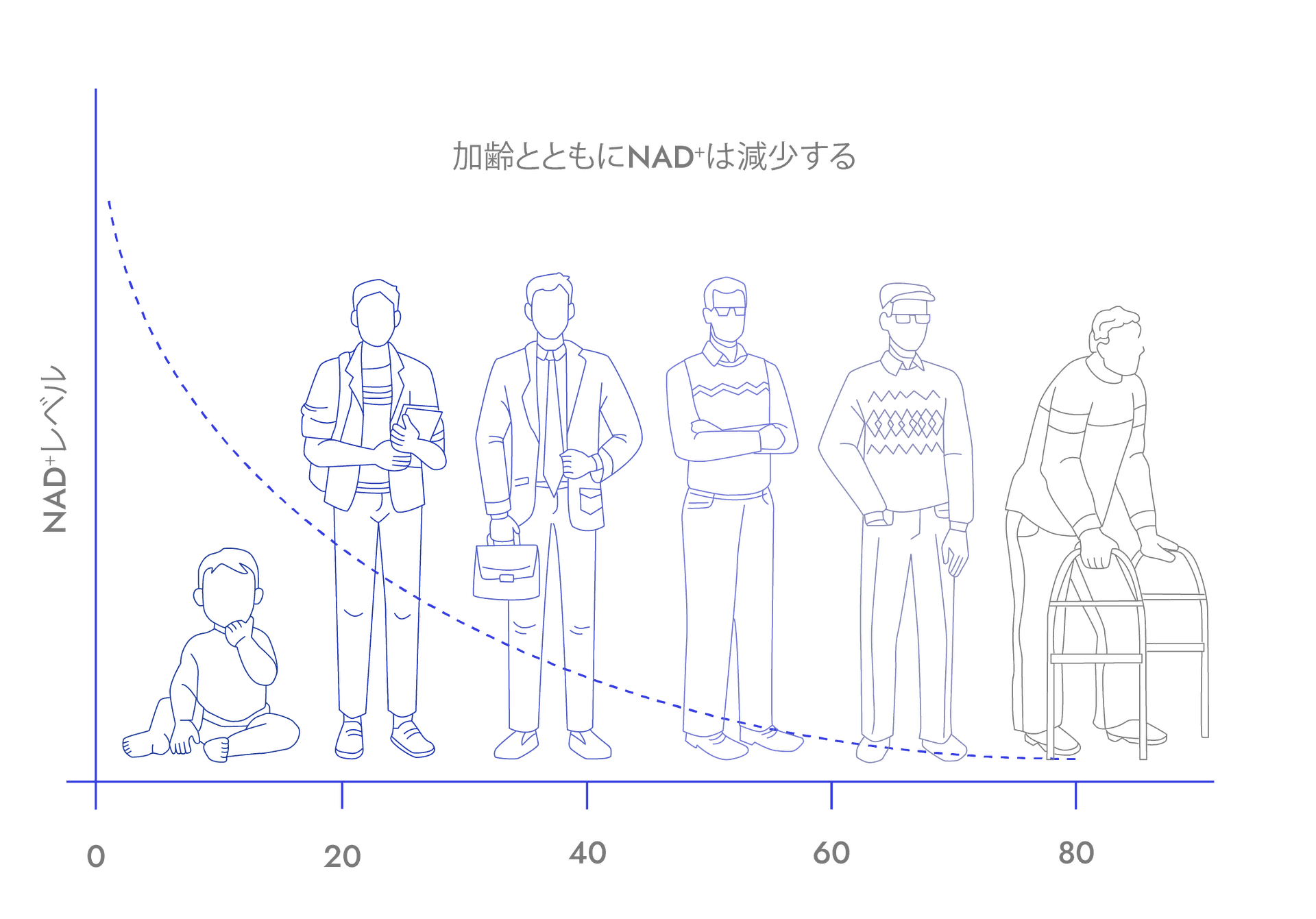
While changes in NAD⁺ levels in other organs are still being uncovered, most human clinical studies so far point to a trend of age-related NAD⁺ reduction. Reduced NAD⁺ levels lower the NAD⁺/NADH redox ratio, shifting our body toward a more reduced state (also known as 'pseudo-hypoxia' state), which is associated with a wide range of age-related pathologies.Consequently, strategies to replenish NAD⁺ holds immense potential to ameliorate the multiple key hallmarks of aging.
NMN:
A Powerful Intervention to Counteract Age-Related NAD⁺ Decline
The anti-aging field has made significant progress in identifying strategies to restore declining NAD⁺ levels. These range from lifestyle interventions like caloric restriction and exercise, which naturally elevate NAD⁺, to more targeted approaches such as intravenous NAD⁺ drips.
Caloric restriction and exercise, while beneficial, may be impractical for frail elderly individuals due to risks of malnutrition, physical demands, and poor adherence.
Intravenous NAD⁺ drips offer potency but are costly, low in reagent stability, require medical supervision owing to possible side effects, and lack robust long-term efficacy and safety data.
As a result, supplementation with NAD⁺ precursors has emerged as a popular approach to boosting NAD⁺ levels.
At MotoGene, we understand that age-related NAD⁺ decline results from a complex interplay of factors, including
Reduced activity of biosynthetic enzymes
Limited availability of NAD⁺ precursors
Increased consumption of NAD⁺by enzymes
Redox imbalance
Mitochondrial dysfunction
Defects in NAD⁺/NAM recycling process
NMN (also known as ‘β-NMN’ or ‘beta form of NMN’) is a derivative of vitamin B3 that is found naturally in various food sources, including plant and animal products. It is also a bioactive nucleotide that is present in the nucleus, cytosol and mitochondria within our cells
To address these root causes, we leverage a well-established, effective, and safe approach—oral supplementation with NMN (Nicotinamide MonoNucleotide), a key NAD⁺ precursor.
Accelerates NAD⁺ depletion

NMN:
A Powerful Intervention to Counteract Age-Related NAD⁺ Decline
The anti-aging field has made significant progress in identifying strategies to restore declining NAD⁺ levels. These range from lifestyle interventions like caloric restriction and exercise, which naturally elevate NAD⁺, to more targeted approaches such as intravenous NAD⁺ drips.

Caloric restriction and exercise, while beneficial, may be impractical for frail elderly individuals due to risks of malnutrition, physical demands, and poor adherence.

Intravenous NAD⁺ drips offer potency but are costly, low in reagent stability, require medical supervision owing to possible side effects, and lack robust long-term efficacy and safety data.
As a result, supplementation with NAD⁺ precursors has emerged as a popular approach to boosting NAD⁺ levels.
At MotoGene, we understand that age-related NAD⁺ decline results from a complex interplay of factors, including
Limited availability of NAD⁺ precursors
Reduced activity of biosynthetic enzymes
Increased consumption of NAD⁺by enzymes
Redox imbalance
Mitochondrial dysfunction
Defects in the recycling process
Accelerates NAD⁺ depletion
To address these root causes, we leverage a well-established, effective, and safe approach—oral supplementation with NMN (Nicotinamide MonoNucleotide), a key NAD⁺ precursor.

NMN (also known as ‘β-NMN’ or ‘beta form of NMN’) is a derivative of vitamin B3 that is found naturally in various food sources, including plant and animal products. It is also a bioactive nucleotide that is present in the nucleus, cytosol and mitochondria within our cells.
Why is NMN a potential game-changer for boosting NAD⁺?
EFFICIENCY OF NMN
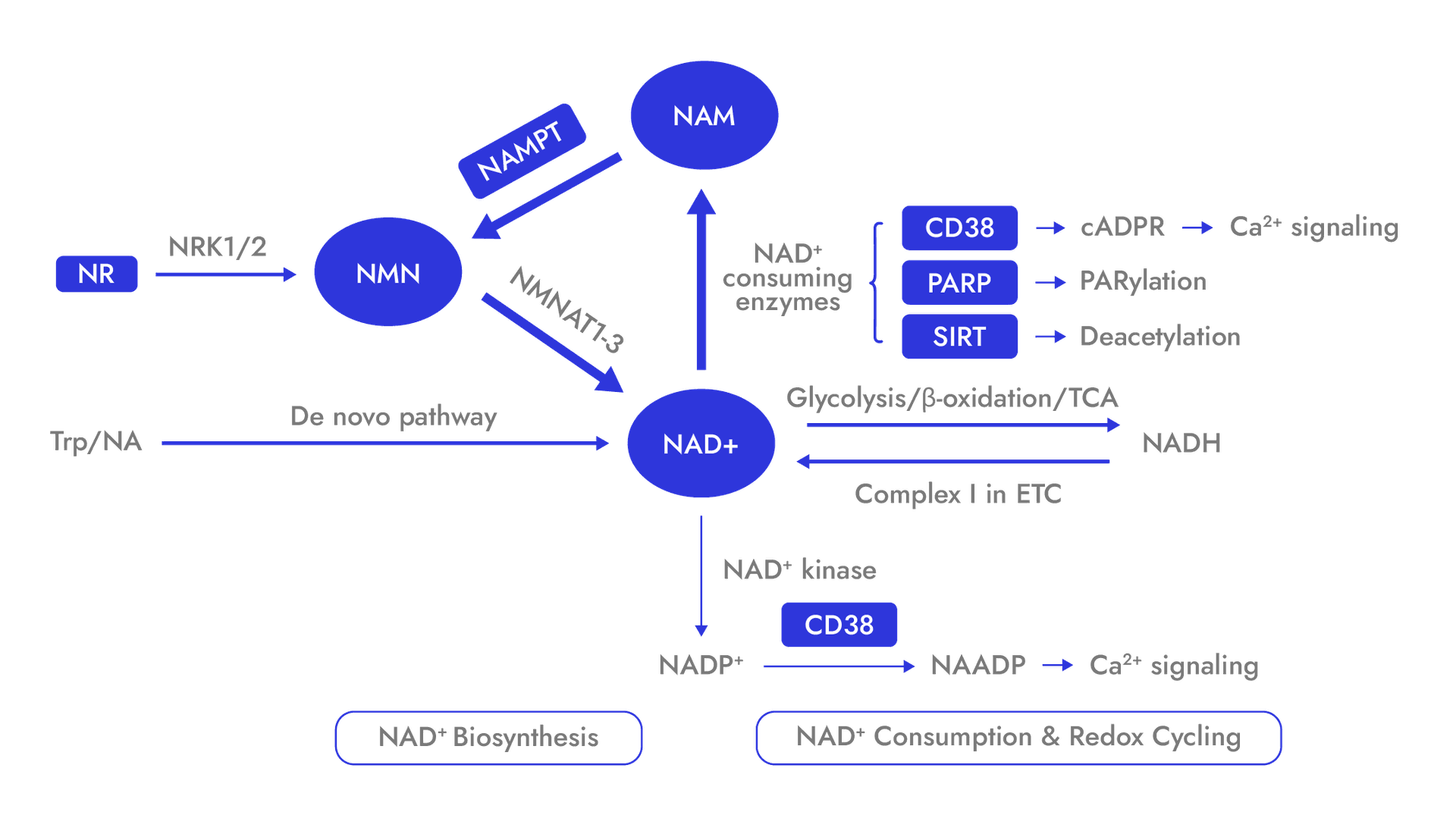
Unlike other NAD⁺ precursors, NMN takes the direct route to NAD⁺ synthesis. Once inside the cell, NMN is rapidly converted into NAD⁺ in a single enzymatic step, catalyzed by NMNAT enzymes within the NAD⁺ salvage pathway — the body’s primary and most efficient route for NAD⁺ biosynthesis. What sets NMN apart even further? It bypasses NAMPT, the rate-limiting enzyme in NAD⁺ production. By avoiding this metabolic bottleneck, NMN has the potential to elevate intracellular NAD⁺ levels more efficiently than other precursors like nicotinamide.
Importantly, multiple human clinical trials have demonstrated that oral NMN supplementation effectively increases NAD⁺ levels in the blood fractions (plasma, peripheral blood mononuclear cells or whole blood) of both healthy individuals and those with health conditions such as hypertension. However, the effects of NMN supplementation on other tissues and organs remain variable and are still under active investigation.
SAFETY OF NMN
Numerous human clinical trials have evaluated the safety of oral NMN supplementation, with most reporting that it is well-tolerated and safe at doses ranging from as low as 100 mg to as high as 1250 mg.
These studies consistently show that NMN supplementation does not cause significant adverse effects or changes in body temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, or oxygen saturation.
Additionally, no notable changes have been observed in ocular or neurological parameters, nor in blood and urine laboratory results. These safety outcomes have been observed in both healthy participants and those with existing health conditions.
Why MotoGene Stands Out for NMN Supplement Innovation and Development?
UNIQUE FORMULATION
We understand that no single supplement can address all aging symptoms. That is why we leverage cutting-edge science to develop NMN supplements tailored to individual conditions. By combining NMN with potent, synergistic ingredients, we unlock its full potential to meet the specific needs of our customers.
Our dosing strategies are carefully selected based on validated clinical trials, ensuring consistent efficacy across a range of consumers. Additionally, we focus on the convenience and usability of our products — our formulations come in an easily dissolved powder form, ideal for the elderly or individuals who struggle with swallowing large pills or capsules.
ONGOING INNOVATION
While oral NMN supplementation has a strong safety profile, it is essential to recognize that NAD⁺ levels are tightly regulated by the body’s homeostatic mechanisms. To prevent unintended metabolic consequences, MotoGene remains at the forefront of research, continuously evaluating the latest scientific advancements.
In our product development, we collaborate closely with various experts to rigorously assess NMN safety, including potential overdose effects, possible interactions with medications, and its impact on individuals with pre-existing conditions. By staying updated on the benefits, risks, and pharmacology of NMN, we design thoughtful, evidence-based formulations that are both safe and effective in promoting a healthier life.
MotoGene is committed to a science-driven approach — our goal is not merely to increase NAD⁺ levels indiscriminately but to strategically restore them to youthful levels for optimal health effects.

STRUCTURAL INTEGRITY
NMN stability is a critical concern, as the molecule is inherently sensitive to degradation, as influenced by various environmental factors. Since NMN structural integrity determines its efficacy, we have invested heavily in optimizing pH, temperature, and humidity control — from raw material selection to manufacturing and logistics — to ensure we deliver NMN in its most intact form.
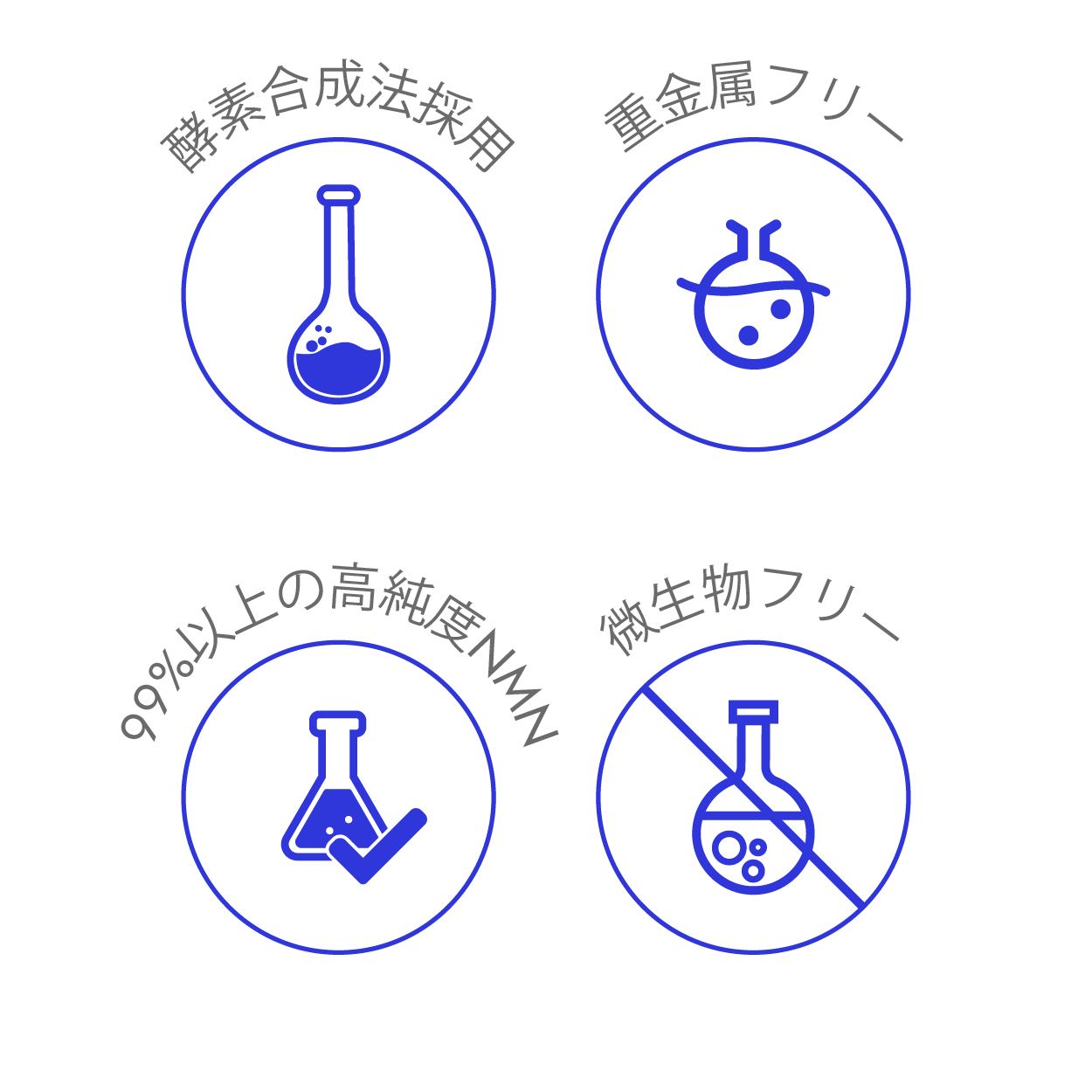
NMN PURITY 99%+
We uphold the highest standards for NMN purity for delivering reliable and effective supplementation. Our manufacturing process is designed to eliminate contaminants and by-products, with rigorous analytical testing to verify purity in every batch. Our NMN is enzymatically synthesized, free from microbes and heavy metals, and guaranteed to be at least 99.0 – 99.7% pure, as confirmed by HPLC assays conducted by two independent laboratories.
At MotoGene, we develop healthspan-promoting NMN supplements with the utmost care and expertise, prioritizing both safety and efficacy. Our commitment to quality includes meticulous attention to ingredient purity, structural integrity, pharmacology, and formulation. We take pride in our thoughtful approach to product development—so much so that we personally use the very supplements we create.
**The content on this page has been carefully curated by the R&D team. Last updated: March 7, 2025**
Why is NMN a potential game-changer for boosting NAD⁺?
EFFICIENCY OF NMN
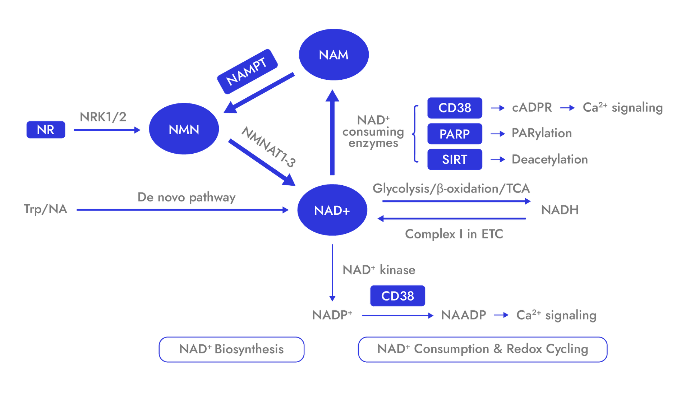
Unlike other NAD⁺ precursors, NMN takes the direct route to NAD⁺ synthesis. Once inside the cell, NMN is rapidly converted into NAD⁺ in a single enzymatic step, catalyzed by NMNAT enzymes within the NAD⁺ salvage pathway — the body’s primary and most efficient route for NAD⁺ biosynthesis. What sets NMN apart even further? It bypasses NAMPT, the rate-limiting enzyme in NAD⁺ production. By avoiding this metabolic bottleneck, NMN has the potential to elevate intracellular NAD⁺ levels more efficiently than other precursors like nicotinamide.
Importantly, multiple human clinical trials have demonstrated that oral NMN supplementation effectively increases NAD⁺ levels in the blood fractions (plasma, peripheral blood mononuclear cells or whole blood) of both healthy individuals and those with health conditions such as hypertension. However, the effects of NMN supplementation on other tissues and organs remain variable and are still under active investigation.
SAFETY OF NMN
Numerous human clinical trials have evaluated the safety of oral NMN supplementation, with most reporting that it is well-tolerated and safe at doses ranging from as low as 100 mg to as high as 1250 mg.
These studies consistently show that NMN supplementation does not cause significant adverse effects or changes in body temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, or oxygen saturation.
Additionally, no notable changes have been observed in ocular or neurological parameters, nor in blood and urine laboratory results. These safety outcomes have been observed in both healthy participants and those with existing health conditions.
Why MotoGene Stands Out for NMN Supplement Innovation and Development?
At MotoGene, we develop healthspan-promoting NMN supplements with the utmost care and expertise, prioritizing both safety and efficacy. Our commitment to quality includes meticulous attention to ingredient purity, structural integrity, pharmacology, and formulation. We take pride in our thoughtful approach to product development—so much so that we personally use the very supplements we create.
NMN PURITY 99%+
We uphold the highest standards for NMN purity for delivering reliable and effective supplementation. Our manufacturing process is designed to eliminate contaminants and by-products, with rigorous analytical testing to verify purity in every batch. Our NMN is enzymatically synthesized, free from microbes and heavy metals, and guaranteed to be at least 99.0 – 99.7% pure, as confirmed by HPLC assays conducted by two independent laboratories.

STRUCTURAL INTEGRITY
NMN stability is a critical concern, as the molecule is inherently sensitive to degradation, as influenced by various environmental factors. Since NMN structural integrity determines its efficacy, we have invested heavily in optimizing pH, temperature, and humidity control — from raw material selection to manufacturing and logistics — to ensure we deliver NMN in its most intact form.
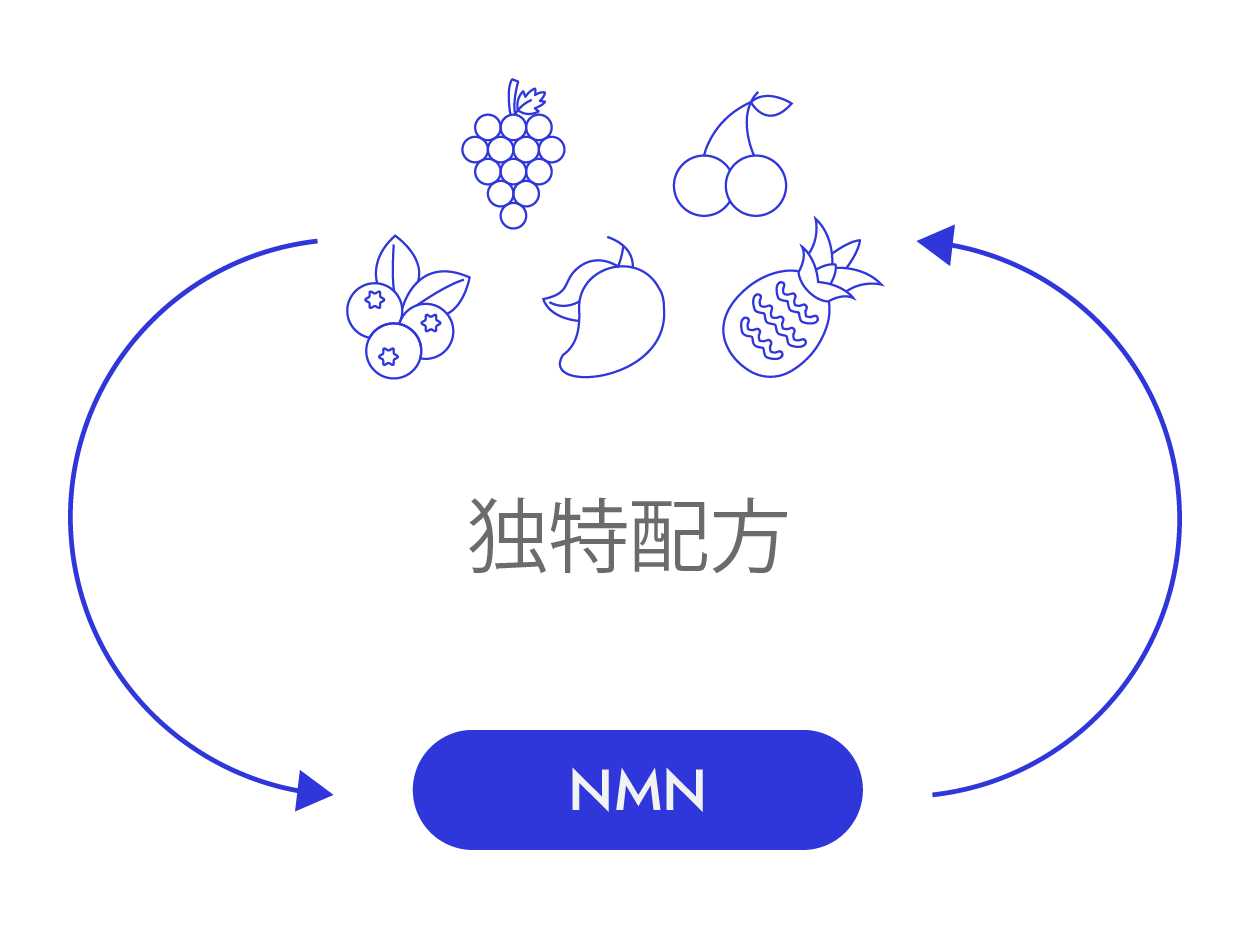
UNIQUE FORMULATION
We understand that no single supplement can address all aging symptoms. That is why we leverage cutting-edge science to develop NMN supplements tailored to individual conditions. By combining NMN with potent, synergistic ingredients, we unlock its full potential to meet the specific needs of our customers.
Our dosing strategies are carefully selected based on validated clinical trials, ensuring consistent efficacy across a range of consumers. Additionally, we focus on the convenience and usability of our products — our formulations come in an easily dissolved powder form, ideal for the elderly or individuals who struggle with swallowing large pills or capsules.
ONGOING INNOVATION
While oral NMN supplementation has a strong safety profile, it is essential to recognize that NAD⁺ levels are tightly regulated by the body’s homeostatic mechanisms. To prevent unintended metabolic consequences, MotoGene remains at the forefront of research, continuously evaluating the latest scientific advancements.
In our product development, we collaborate closely with various experts to rigorously assess NMN safety, including potential overdose effects, possible interactions with medications, and its impact on individuals with pre-existing conditions. By staying updated on the benefits, risks, and pharmacology of NMN, we design thoughtful, evidence-based formulations that are both safe and effective in promoting a healthier life.

MotoGene is committed to a science-driven approach — our goal is not merely to increase NAD⁺ levels indiscriminately but to strategically restore them to youthful levels for optimal health effects.
**The content on this page has been carefully curated by the R&D team. Last updated: March 7, 2025**